EvadeML-Zoo Benchmarking and Visualization AE Tool is released
We are releasing EvadeML-Zoo: A Benchmarking and Visualization Tool for Adversarial Examples (with 8 pretrained deep models+ 9 state-of-art attacks).
Tool Github URL
About
We have designed and implemented EvadeML-Zoo, a benchmarking and visualization tool for research on adversarial machine learning. The goal of EvadeML-Zoo is to ease the experimental setup and help researchers evaluate and verify their results.
EvadeML-Zoo has a modular architecture and is designed to make it easy to add new datasets, pre-trained target models, attack or defense algorithms. The code is open source under the MIT license.
We have integrated three popular datasets: MNIST, CIFAR-10 and ImageNet- ILSVRC with a simple and unified interface. We offer several representative pre-trained models with state-of-the-art accuracy for each dataset including two pre-trained models for ImageNet-ILSVRC: the heavy Inception-v3 and and the lightweight MobileNet. We use Keras to access the pre-trained models because it provides a simplified interface and it is compatible with TensorFlow, which is a flexible tool for implementing attack and defense techniques.
We have integrated several existing attack algorithms as baseline for the upcoming new methods, including FGSM, BIM, JSMA, Deepfool, Universal Adversarial Perturbations, and Carlini and Wagner’s algorithms.
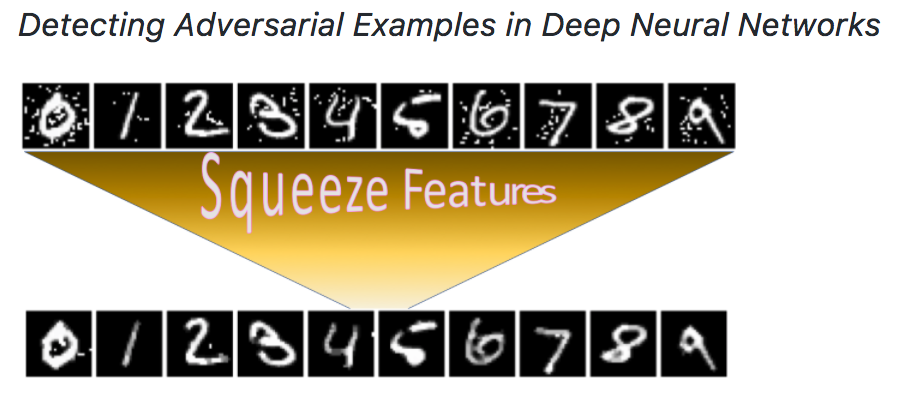
We have integrated our “feature squeezing” based detection framework in this toolbox. Formulating detecting adversarial examples as a binary classification task, we first construct a balanced dataset with equal number of legitimate and adversarial examples, and then split it into training and test subsets. A detection method has full access to the training set but no access to the labels of the test set. We measure the TPR and FPR on the test set as the benchmark detection results. Our Feature Squeezing functions as the detection baseline. Users can easily add more detection methods using our framework.
Besides, the tool comes with an interactive web-based visualization module adapted from our previous ADVERSARIAL-PLAYGROUND package. This module enables better understanding of the impact of attack algorithms on the resulting adversarial sample; users may specify attack algorithm parameters for a variety of attack types and generate new samples on-demand. The interface displays the resulting adversarial example as compared to the original, classification likelihoods, and the influence of a target model throughout layers of the network.
Citations
@inproceedings{Xu0Q18,
author = {Weilin Xu and
David Evans and
Yanjun Qi},
title = {Feature Squeezing: Detecting Adversarial Examples in Deep Neural Networks},
booktitle = {25th Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, {NDSS}
2018, San Diego, California, USA, February 18-21, 2018},
year = {2018},
crossref = {DBLP:conf/ndss/2018},
url = {http://wp.internetsociety.org/ndss/wp-content/uploads/sites/25/2018/02/ndss2018\_03A-4\_Xu\_paper.pdf},
timestamp = {Thu, 09 Aug 2018 10:57:16 +0200},
biburl = {https://dblp.org/rec/bib/conf/ndss/Xu0Q18},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, https://dblp.org}
}
Support or Contact
Having troubl with our tools? Please contact Weilin and we’ll help you sort it out.
