Journal Machine Learning - SIMULE R package is released!
Tool SIMULE: A constrained l1 minimization approach for estimating multiple Sparse Gaussian or Nonparanormal Graphical Models
R package: simule
install.packages("simule")
library(simule)
demo(simule)
Package Manual
GitHub
Paper: @Arxiv | @Mach Learning
Talk
Abstract
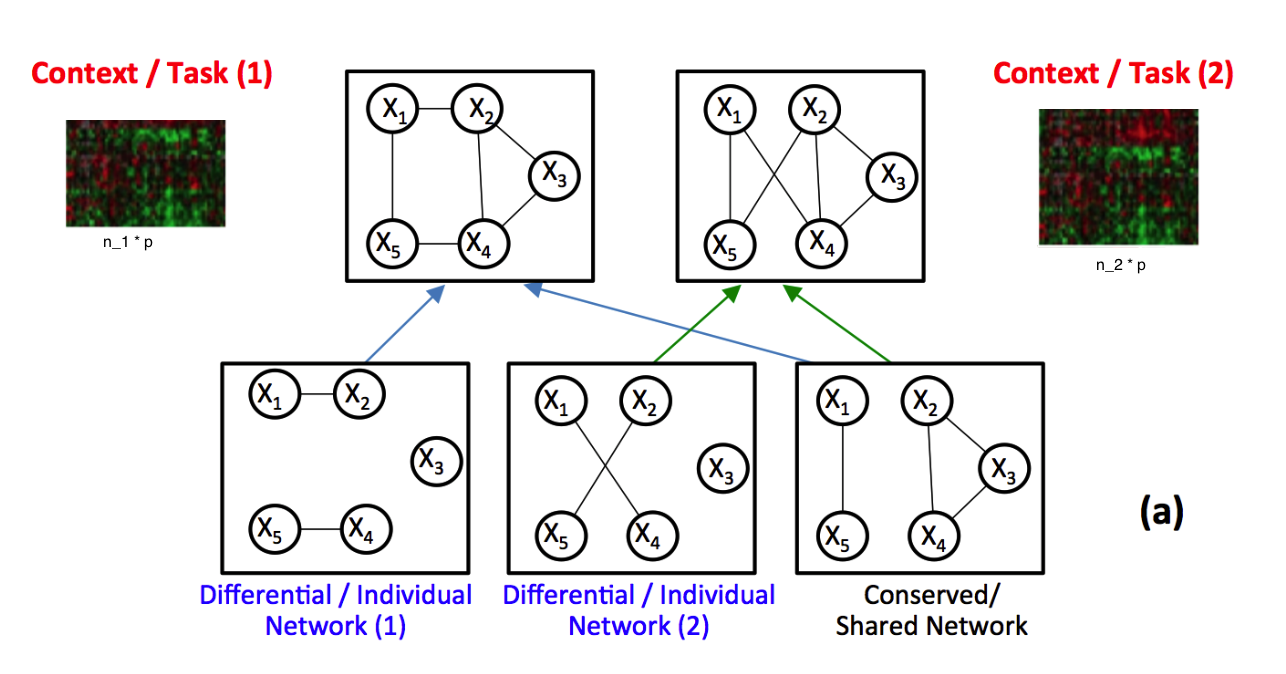
Identifying context-specific entity networks from aggregated data is an important task, arising often in bioinformatics and neuroimaging. Computationally, this task can be formulated as jointly estimating multiple different, but related, sparse Undirected Graphical Models (UGM) from aggregated samples across several contexts. Previous joint-UGM studies have mostly focused on sparse Gaussian Graphical Models (sGGMs) and can’t identify context-specific edge patterns directly. We, therefore, propose a novel approach, SIMULE (detecting Shared and Individual parts of MULtiple graphs Explicitly) to learn multi-UGM via a constrained L1 minimization. SIMULE automatically infers both specific edge patterns that are unique to each context and shared interactions preserved among all the contexts. Through the L1 constrained formulation, this problem is cast as multiple independent subtasks of linear programming that can be solved efficiently in parallel. In addition to Gaussian data, SIMULE can also handle multivariate Nonparanormal data that greatly relaxes the normality assumption that many real-world applications do not follow. We provide a novel theoretical proof showing that SIMULE achieves a consistent result at the rate O(log(Kp)/n_{tot}). On multiple synthetic datasets and two biomedical datasets, SIMULE shows significant improvement over state-of-the-art multi-sGGM and single-UGM baselines.
Citations
@Article{Wang2017,
author="Wang, Beilun and Singh, Ritambhara and Qi, Yanjun",
title="A constrained L1 minimization approach for estimating multiple sparse Gaussian or nonparanormal graphical models",
journal="Machine Learning",
year="2017",
month="Oct",
day="01",
volume="106",
number="9",
pages="1381--1417",
abstract="Identifying context-specific entity networks from aggregated data is an important task, arising often in bioinformatics and neuroimaging applications. Computationally, this task can be formulated as jointly estimating multiple different, but related, sparse undirected graphical models(UGM) from aggregated samples across several contexts. Previous joint-UGM studies have mostly focused on sparse Gaussian graphical models (sGGMs) and can't identify context-specific edge patterns directly. We, therefore, propose a novel approach, SIMULE (detecting Shared and Individual parts of MULtiple graphs Explicitly) to learn multi-UGM via a constrained L1 minimization. SIMULE automatically infers both specific edge patterns that are unique to each context and shared interactions preserved among all the contexts. Through the L1 constrained formulation, this problem is cast as multiple independent subtasks of linear programming that can be solved efficiently in parallel. In addition to Gaussian data, SIMULE can also handle multivariate Nonparanormal data that greatly relaxes the normality assumption that many real-world applications do not follow. We provide a novel theoretical proof showing that SIMULE achieves a consistent result at the rate
log (Kp)/(n_tot). On multiple synthetic datasets and two biomedical datasets, SIMULE shows significant improvement over state-of-the-art multi-sGGM and single-UGM baselines
(SIMULE implementation and the used datasets @ https://github.com/QData/SIMULE ).",
issn="1573-0565",
doi="10.1007/s10994-017-5635-7",
url="https://doi.org/10.1007/s10994-017-5635-7"
}
Support or Contact
Having trouble with our tools? Please contact Beilun and we’ll help you sort it out.
